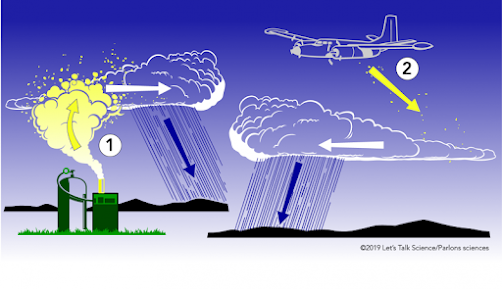
Cloud seeding
Cloud seeding, also known as artificial rain technology, is a weather modification technique aimed at enhancing precipitation in specific regions. It involves the intentional introduction of certain substances into clouds to stimulate the formation and growth of water droplets or ice crystals, which eventually lead to increased rainfall or snowfall.
Process
The process of cloud seeding relies on the concept of nucleation, where the seeding materials act as catalysts for the condensation or freezing of water vapor present in the clouds. By introducing these materials, such as silver iodide or potassium iodide, into the clouds, it is believed that more cloud droplets or ice crystals can form, increasing the chances of precipitation.
Various methods
Cloud seeding can be implemented through various methods, including ground-based generators, aircraft, or rockets. Ground-based generators release the seeding materials into the air, while aircraft or rockets disperse them from above the clouds. The choice of method depends on factors like the desired coverage area, cloud type, and prevailing weather conditions.
Advantages of Cloud Seeding:
1. Increased Precipitation: The primary advantage of cloud seeding is the potential to enhance precipitation in regions experiencing water scarcity or drought conditions. By increasing rainfall or snowfall, cloud seeding can help replenish water resources and support agricultural needs.
2. Water Resource Management: Cloud seeding can be used as a tool for water resource management, allowing for more efficient allocation and distribution of water supplies. It provides a means to potentially increase water availability in specific regions, reducing reliance on natural precipitation patterns.
3. Mitigating Wildfires: In certain situations, cloud seeding can be used as a means to reduce the risk and intensity of wildfires. By inducing rainfall over fire-prone areas, cloud seeding can help dampen dry conditions and reduce the spread of wildfires.
Disadvantages and Considerations of Cloud Seeding:
1. Uncertain Effectiveness:
The effectiveness of cloud seeding is still a subject of scientific debate. While some studies have shown positive results, others have reported limited or inconclusive impacts. The success of cloud seeding can be influenced by various factors, such as cloud type, atmospheric conditions, and the availability of natural cloud nuclei.
2. Environmental Impact:
Cloud seeding involves the introduction of seeding materials, such as silver iodide or potassium iodide, into the atmosphere. While studies have generally found no significant adverse effects on human health or the environment, there are ongoing efforts to better understand any potential long-term environmental impacts and unintended consequences of cloud seeding.
3. Ethical and Legal Considerations:
The use of cloud seeding raises ethical and legal considerations. Proper regulations and guidelines must be followed to ensure responsible and safe implementation. Transparency, accountability, and stakeholder engagement are important in addressing concerns related to the ownership and distribution of water resources.
4. Cost and Infrastructure:
Implementing cloud seeding operations can be costly, requiring specialized equipment, trained personnel, and ongoing monitoring and evaluation. The cost-effectiveness of cloud seeding projects must be carefully assessed, considering the potential benefits and the specific needs of the targeted region.
5. Localized Impact:
Cloud seeding is a localized intervention, and its effects are limited to the targeted region. It does not address broader issues related to climate change and global warming, which require comprehensive and systemic approaches focused on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices.
It's important to note that cloud seeding is typically used as a supplemental tool within a broader water resource management strategy and should not be viewed as a standalone solution. Its implementation should be guided by scientific research, careful planning, and adherence to regulations and guidelines.
Results
The effectiveness of cloud seeding is a topic of ongoing scientific research and debate. While some studies have reported positive results, demonstrating increased precipitation in seeded areas, others have yielded inconclusive or mixed outcomes. The success of cloud seeding can be influenced by factors such as the type of clouds targeted, atmospheric conditions, and the availability of natural cloud nuclei.
Cloud seeding is often employed in regions experiencing water scarcity, drought conditions, or as a part of water resource management strategies. However, it is important to note that cloud seeding is typically used as a supplemental tool and not as a standalone solution. It is meant to complement other water management practices and is subject to regulations and guidelines to ensure its safe and responsible use.
A potential avenue for influencing weather patterns
Overall, cloud seeding offers a potential avenue for influencing weather patterns and increasing precipitation in specific areas. Ongoing research and advancements in technology continue to refine our understanding of cloud seeding and its potential applications in water resource management.
Experiments:
Vincent J. Schaefer
One of the early pioneers of cloud seeding was Vincent J. Schaefer, an American chemist, who conducted experiments in the 1940s. Schaefer's experiments involved introducing dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) into clouds, which resulted in the formation of ice crystals and subsequent precipitation.
Bernard Vonnegut
Another notable figure in the development of cloud seeding is Bernard Vonnegut, an American atmospheric scientist and brother of renowned author Kurt Vonnegut. Bernard Vonnegut discovered the role of silver iodide in cloud seeding in the early 1950s. Silver iodide has a similar crystal structure to ice, making it an effective nucleating agent for the formation of ice crystals in clouds.
Various organizations
Since then, cloud seeding research and development have been carried out by various organizations, including government agencies, universities, and private companies around the world. These efforts have contributed to further understanding the potential of cloud seeding and refining the techniques and materials used.
It's important to note that cloud seeding is an ongoing area of research, and the effectiveness and environmental impacts of the technique are still subjects of scientific investigation and debate.
The effect of cloud seeding on global warming
The effect of cloud seeding on global warming is a complex and debated topic. Cloud seeding itself is primarily focused on modifying local weather patterns by enhancing precipitation, and its direct impact on global climate change is considered minimal. However, there are potential indirect effects and considerations to take into account:
1. Albedo Effect:
Clouds play a crucial role in the Earth's energy balance by reflecting sunlight back into space. This reflective property is known as the albedo effect. Cloud seeding could potentially alter cloud properties, such as cloud thickness, height, and composition, which may affect the overall reflectivity of clouds and, in turn, the Earth's energy balance. However, the magnitude and direction of this effect are still uncertain and highly dependent on specific cloud and atmospheric conditions.
2. Regional Climate Effects:
Cloud seeding is typically implemented on a local or regional scale to increase rainfall or snowfall in specific areas. While cloud seeding may temporarily modify weather patterns and precipitation distribution in the targeted region, its impact on global climate patterns, including global warming, is considered negligible due to the localized nature of the intervention.
3. Uncertainties and Unintended Consequences:
Cloud seeding involves introducing foreign substances into the atmosphere, such as silver iodide. While studies have generally found no significant adverse effects on human health or the environment, there is ongoing research to better understand any potential long-term environmental impacts and unintended consequences of cloud seeding. It is important to exercise caution and adhere to proper regulations and guidelines when conducting cloud seeding operations.
It's crucial to note that global warming and climate change are complex phenomena influenced by a range of factors, including greenhouse gas emissions, land use changes, and natural climate variability. While cloud seeding may have localized effects on weather and precipitation, its contribution to global warming is considered negligible compared to the broader factors driving climate change. Efforts to address global warming primarily focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices across various sectors of society.